by Adelle M. Banks, RNS | May 5, 2022 | Commentary, Headline News |

(RNS) — Sunday school and other Christian education programs have suffered during the COVID-19 pandemic, with half of congregations surveyed saying their programs were disrupted.
A March 2022 survey by the Hartford Institute for Religion Research found that larger churches with more than 100 people were more successful in maintaining their educational programming for children and youth, often using in-person or hybrid options. Smaller churches, especially those with 50 or fewer attendees, were least likely to say they continued religious education without disruption.
Scott Thumma, principal investigator of the Exploring the Pandemic Impact on Congregations project, said the findings echoed concerns about general education of schoolchildren, where researchers have seen declines in learning over the last two years.
“My sense is that people knew what good robust Sunday school was or what a successful vacation Bible school was,” said Thumma, drawing in part on open-ended comments in the survey. “And they couldn’t parallel that using Zoom or using livestreaming or using take-home boxes of activities. It just wasn’t the same thing. And so when they evaluated it, it just didn’t measure up to what they previously knew as the standard of a good quality religious education program.”
The findings are the third installment in the five-year project, a collaboration with 13 denominations from the Faith Communities Today cooperative partnership and institute staffers.
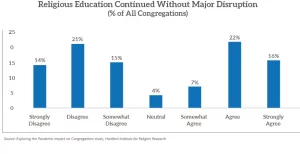
The new report, “Religious Education During the Pandemic: A Tale of Challenge and Creativity,” is based on responses from 615 congregations across 31 denominations.
Comparing data from 2019, churches surveyed in March 2022 reported that the attendance of their religious education programs had decreased an average of 30% among children younger than 13 and 40% among youth, ages 13-17.
“Analysis showed that those who closed their programs had the greatest decline in involvement even after they restarted,” the new report states. “Likewise, churches that moved religious education online lost a higher percentage of participants than churches who modified their efforts with safety protocols but continued meeting in person either outdoors or in small groups.”
The report notes that it’s not surprising the smallest churches experienced the most disruption in their religious education, given the decline in volunteer numbers and additional stresses on clergy during the pandemic.
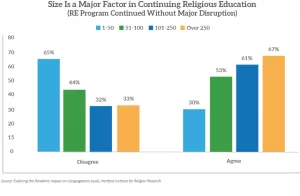
“In the smallest churches (1-50 attendees) pastors were most likely in charge of the religious education programs, while for those between 51 and 100 worshippers, volunteers bore the bulk of leadership responsibilities,” according to the report.
Overall, evangelical churches reported experiencing the least disruption to their educational programs, while mainline churches reported the most, followed by Catholic and Orthodox congregations.
Vacation Bible school, long a staple of congregational outreach to local communities, has also been shaken by COVID-19. More than a third (36%) of churches offered such programs prior to the pandemic. That number decreased to 17% in 2020 and jumped back to 36% in the summer of 2021. Slightly less than a third (31%) reported VBS plans for 2022.
While children’s programming was greatly affected by congregational change during the pandemic, adult religious programs saw the smallest decreases compared with pre-pandemic levels, with a quarter growing since 2019 and an almost equal percentage (23%) remaining even.
But, as with children’s programs, churches with 50 or fewer worshippers saw the greatest loss in adult religious education, while those with more than 250 in worship attendance increased their adult programs by an average of 19%.
Some congregations reported moving Sunday school activities to weeknights or vacation Bible schools from weekday mornings to later hours, with mixed results.
“One said they ‘went from a typical 200+ kids to about 35,’” the report notes, and they “’shortened the number of days and moved VBS to the afternoon.’”
Thumma said innovations including intergenerational and kid-friendly programming helped sustain programs for people of all ages in some congregations. These included revamping of the children’s message time during worship to be more inclusive or older members greeting children who run by during Zoom sessions. Some churches called their all-ages activities “messy church” or “Sunday Funday” as they used interactive educational events.
“It becomes, out of necessity, intergenerational because that allows you to have robust energy and lots of people there,” he said. “But it really is directed at the kids being involved in the life of the congregation in a way that isn’t, like, ‘OK, you go to your class’ and ‘you go to your classes,’ and the classes don’t ever mingle.”
Whether creative steps such as new intergenerational activity will continue remains to be seen, Thumma added.
“I think it should because that’s a valuable strategy,” he said. “One of the things that we’ve seen in lots of our research is the more intergenerational the congregation is, the more it has a diversity of any degree, the more likely they are to be vital and thriving.”
The findings in the new report of the project, which is funded by the Lilly Endowment, have an estimated overall margin of error of plus or minus 4 percentage points.
READ THIS STORY AT RELIGIONNEWS.COM












