
Clergy divided as Kenya moves to save forest, evict 40,000 settlers

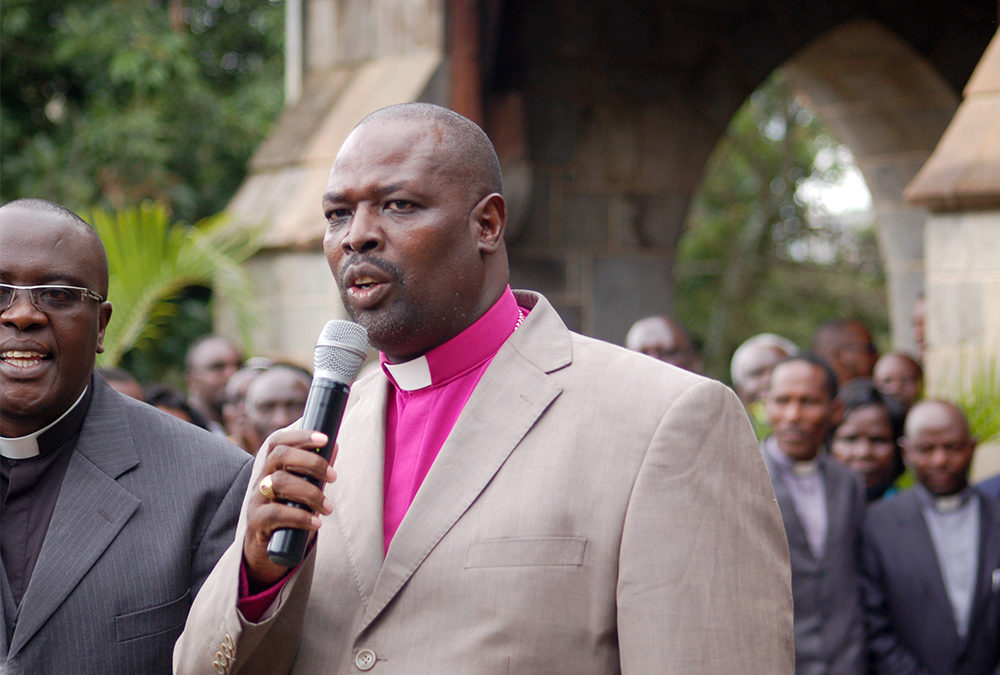
Anglican archbishop Jackson Ole Sapit speaks in Nairobi on May 19, 2016. RNS photo by Fredrick Nzwili
NAIROBI, Kenya – When forest rangers arrived at Mau Forest Complex in June to evict thousands of illegal settlers, frightened villagers started moving out.
Villagers sought refuge at churches, schools and trading centers as smoke billowed from their homes, which were razed in the exercise. Churches, schools and crops have been burned in a clearing process that government officials say will save the main water supply.
Amid the mass clearing, clerics have been pulled into the controversy. Some religious leaders support the evictions, saying they are key to protecting the forest complex as a God-given heritage and an essential ecosystem. Other leaders are opposed, saying the evictions are inhumane.
More than 40,000 farmers and herders have been targeted in the mass eviction. They have been occupying 146,000 hectares (about 360,000 acres) of the 400,000-hectare (988,000-acre) forest land in a section known as Maasai Mau. They had bought pieces of land in what some church leaders describe as politically driven purchases aimed at influencing voting patterns in the region.
Some have lived in the forest for more than 30 years. But with visible massive destruction of the forest and river sources, the government is now forcing residents to move. Concerns include how removal of trees and brush has exacerbated erosion, increased soil in riverbeds and put them at risk of running dry. Communities downstream depend on the rivers to supply drinking water, including for livestock and wildlife living in refuge parks.
In the eviction process, large-scale tea farms have also been shut. Owners have been ordered to let the crop grow into bushes. Some 7,000 residents have been evicted this summer as the government reclaimed 12,000 hectares from them.
Jackson Ole Sapit, the Anglican archbishop of Kenya, told Religion News Service he supports the evictions. He said the forest is a holy ecosystem that must be saved at all costs.
“If we don’t preserve it now, we will soon see communities suffering serious water shortages, and even wildlife and livestock,” he said. “This is very urgent.”
According to Sapit, the forest is home to many rivers that serve important bodies of water, including Lake Victoria, Lake Natron and the River Nile.
The forest “gives life to the Mara River, which is the lifeline of the wildebeests migration, one of the wonders of the world,” said Sapit, referring to the phenomenon in which 1.5 million wildebeests, zebra and antelope make a circular tour between the Serengeti game reserve and the Maasai Mara in Kenya in search of greener pastures. “Killing forest will kill the wildebeest migration.”
Others agree the government is taking necessary steps.
“I think the evictions are a win-win situation for Kenyans — including the settlers,” said the Rev. Charles Odira, a Catholic priest and a conservationist. “It may take time to restore the forest, but in the long run the action will prove very beneficial for the country.”
Kenya’s government has ruled out compensation for forest residents, saying that they settled there illegally. The residents have to look for alternative land to settle or return to their original homelands. Some have been surrendering land title deeds, which government officials claim are fake.
According to Hassan Ole Naado, deputy secretary-general of the Supreme Council of Kenya Muslims, most of the settlers are innocent citizens who were duped by racketeers to purchase the forest land.
“The racketeers used their influence and power to swindle these people. The authorities should pursue them (instead),” said Naado.
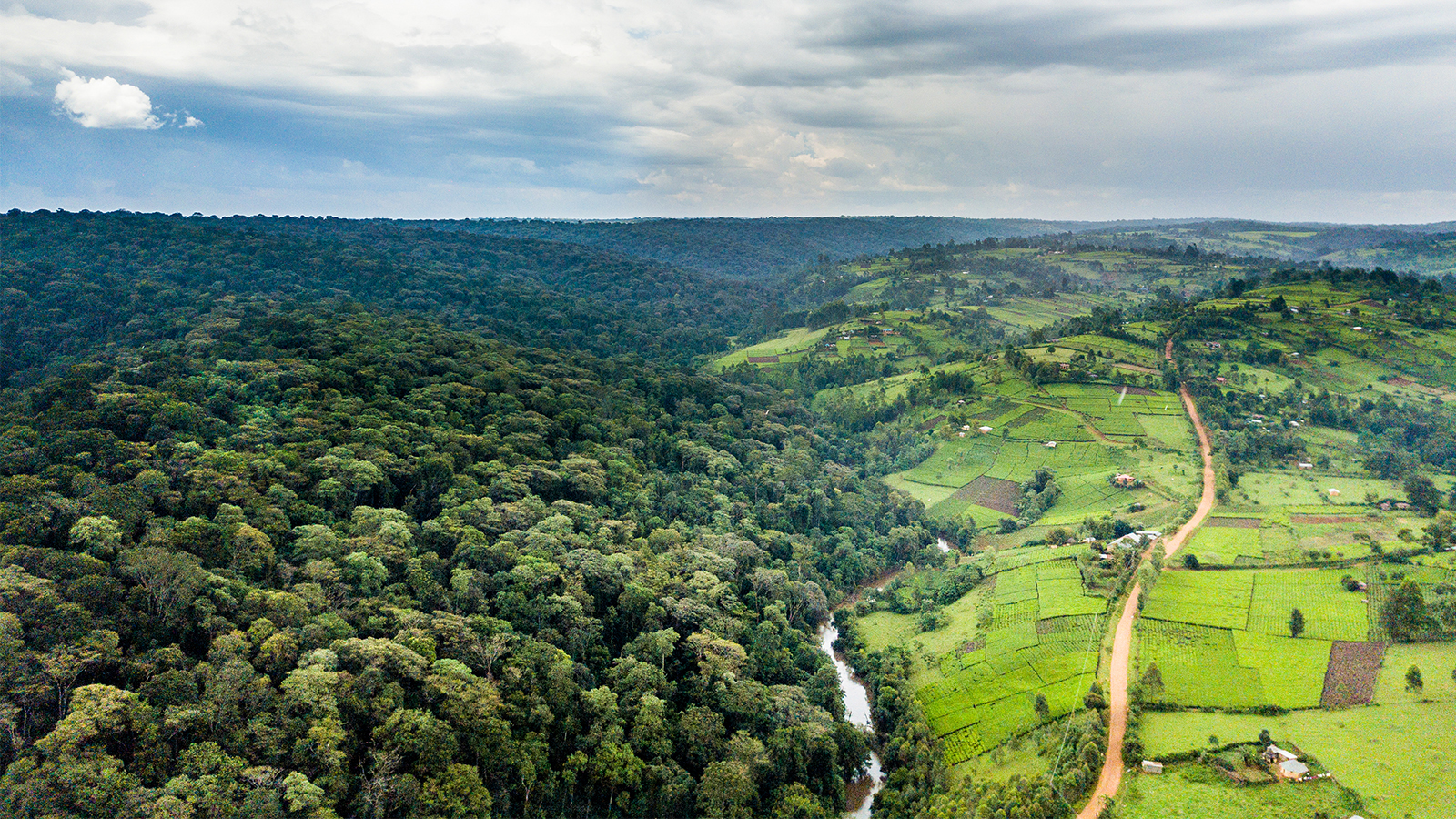

An aerial view of Mau Forest and neighbouring tea estates in western Kenya on Oct. 7, 2017. Photo by Patrick Sheperd/CIFOR/Creative Commons
While the evictions have widespread support in Kenya, some church leaders have raised a red flag. They say they are not opposed to the conservation of the water supply, but they argue the evictions are cruel.
Paul Leleito, a retired bishop of the African Gospel Church, said government authorities have failed to follow a steering commission’s recommendations to clear the area by marking the forest border, determining land ownership and using resources to support residents who are forced to leave.
“My concern is they have enforced the evictions without a proper prior warning,” said Leleito. “Many of those affected by eviction have no shelter and are living in the open where (they) suffer cold nights. Some of them are sick. Children are not going to school.”
Leleito urged the government to give evicted residents time to plan their departure.
“For now, the people should be allowed to harvest the crops they had planted in farms,” said Leleito. “This is not happening, and the crops are likely to go to waste.”
Meanwhile, clerics are warning politicians not to use the evictions to score political points, which they fear is dividing the local communities. Sapit suggested that the forest should be fenced in to prevent future encroachment or illegal settlement.
“We need to look at the greater good and encourage the government to protect the environment,” said Sapit.
The Mau Forest in western Kenya. Map courtesy Google Maps


 Pentecostal pastor James Kyalo of the Machakos region, 40 miles from the capital Nairobi, said his church demands two HIV tests: the first when the couple seeks to start the wedding process; then six months later.
Pentecostal pastor James Kyalo of the Machakos region, 40 miles from the capital Nairobi, said his church demands two HIV tests: the first when the couple seeks to start the wedding process; then six months later.