
Shreveport-Bossier Convention and Tourist Bureau/Flickr, CC BY
Robert E. May, Purdue University
This holiday season, many Americans will tour historic mansions in the Southern United States that are beautifully decked out in traditional wreaths, garlands and mistletoe for Christmas.
At Mount Vernon, George Washington’s Virginia mansion, tourists are promised candlelit tours and a “festive evening” of refreshments, 18th-century dancing and more. Visitors can even meet a re-enactor playing Martha Washington, America’s First Lady.
At the state-run Hofwyl-Broadfield Plantation Historic Site in Brunswick, Georgia, promoters promise attendees a “magical experience” during the holiday event, learning how “Christmas was celebrated on a Southern rice plantation during the 1850s.”
What these tours teach is how rich white Southerners once celebrated Christmas: singing Christmas carols, dancing, drinking the cider brew wassail and enjoying refreshments or formal meals.
Few make a serious effort to tell what Christmas was like for the enslaved workers at these plantations before the American Civil War.
What’s missing?
When the black historian Brandon Byrd visited Belle Meade, a mansion in Nashville, Tennessee, for its Christmas tour a few years ago, he was shocked that the slave community and their harsh realities were barely mentioned. Instead, he reported, the tour guide mostly related “stories about the white men, women and children who woke up to Christmas in the mansion’s plush bedrooms.”
By the American Civil War, nearly four million slaves in all toiled in the southern states, and about a million lived as servants in mansions and as field hands on large plantations with 50 slaves or more. They did almost all the grueling household and field labor that kept these places going, often sleeping and cooking in primitive cabins and working in unhealthy conditions under the threat of the whip.
In fact, the historic mansions hosting Christmas tourists never would have been built without the profits generated by slave labor. The grand Nottoway Plantation and resort in Louisiana, which traditionally puts on a Christmas event, was constructed just before the Civil War by some 155 slave workers.
Fictional tales and memoirs
In researching my 2019 book “Yuletide in Dixie,” I discovered that many historic plantation and mansion sites are reluctant to talk about slavery at their Christmas events. This is partly because administrators want to avoid topics that might make paying guests angry or uncomfortable.
But the omission of black southerners from these holiday tales also stems from pervasive myths about slave life at southern plantations before the Civil War.
For a long time, many people got their ideas about slavery at these places from memoirs, novels and short stories written by white southerners after the Civil War. These stories, now outrageous for their racial stereotypes, not only justified the institution of slavery, they also made it seem like all enslaved people had fun on a southern plantation at holiday time, dancing, singing, laughing and feasting for the holiday season, just as their masters did.
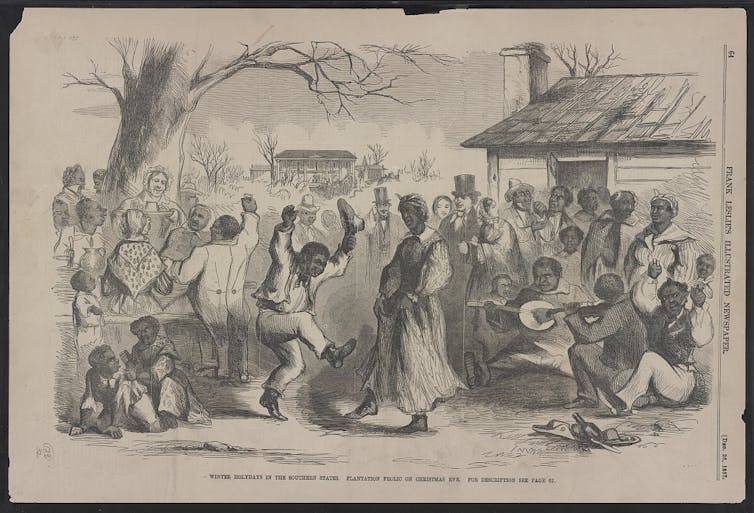

Frank Leslie, in 1857
Susan Dabney Smedes, a white girl who grew up on a Mississippi plantation, published a memoir in 1887 called “Memorials of a Southern Planter” that made slave Christmases sound like wonderful times. Smedes wrote about how slaves wore their best clothes for Christmas, played a word game called “Christmas Gif’” with their white enslavers and drank eggnog their master made for them.
In a fictional tale published in the “Century Magazine” in 1911, an enslaved carpenter named Jerry even turns down the freedom that his master offers him on Christmas because he likes his life as a slave so much, and especially the Christmas present his master specially picks out for him each year.
Many of these memoirs and preposterous short stories and novels about happy slave Christmas experiences were so popular that they were republished in new editions over and over again from the late 1800s and early 1900s until, in some cases, the present.
Smedes’s “Memorials of a Southern Planter” was regularly republished for a century after its first appearance.
Many Americans got falsely pleasant images of slavery and especially slave Christmases from reading these works, and these wrongful impressions not only affected how the public thought and still thinks about slavery but, more specifically, how site administrators at southern historic mansions and plantations planned their Christmas programs.
Whipped and sold on Christmas
I read many documents to find out how slaves actually spent their Christmases. The truth is deeply disturbing.
Mediadrumworld.com
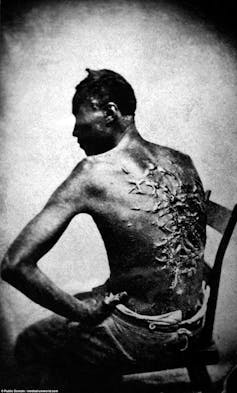
On the one hand, the majority of enslaved people did get some them time off from work during Christmas, as well as feasts and presents. Some got to travel or to get married, privileges that they didn’t get at other times of the year. But these privileges could be withdrawn for any reason at all and many slaves never got them at all.
Slavery was a brutal system of forced labor to enrich those same owners. Even over the holiday, masters kept the power to punish slaves. A photo taken during the Civil War shows a man who was whipped at Christmas. His back was covered with scars, showing that when masters punished the people they held in bondage, they often did so brutally.
There were other cruel forms of punishment. On one South Carolina plantation, a master angry at an enslaved woman he suspected of miscarrying her pregnancy on purpose locked her up for the Christmas holiday.
Masters sometimes forced enslaved workers to get drunk even if they did not want to drink, or wrestle with each other on Christmas simply for the amusement of the master’s family.
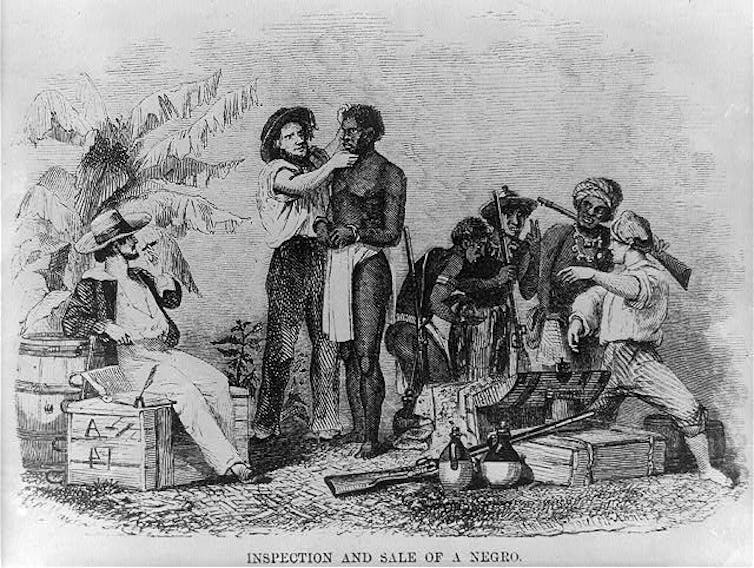

Library of Congress
Likewise, I learned in my research, slaveholders bought and sold plenty of people over the holiday, keeping slave traders busy during Christmas week.
Escapes and panics over slave rebellions
It is revealing that many enslaved black southerners also chose Christmas as the time to try to escape to freedom, despite the difficulties of traveling in cold weather with few supplies.
The famous black liberator Harriet Tubman, for example, helped her three brothers enslaved in Maryland to escape bondage over Christmas in 1854. Obviously, slaves like the Tubman brothers greatly resented their enslavement, or they would not have agreed to leave.
Evidence shows that many slaveholders knew their slaves hated their condition. Although the U.S. never had a major Christmas slave rebellion, southern whites frequently panicked over frequent rumors that their slaves planned to revolt over the holiday. They armed themselves, conducted extra patrols, banned black people from the streets of cities and executed or whipped slaves whose behavior they thought was suspicious.
Panics over Christmas rebellions took place frequently. They were, at times, confined to a state as in Charleston, South Carolina – then a British colony – in 1765. Or, they could spread in the entire American South, as one did in 1856. As I found in my research, Christmas revolt panics continued all the way through the Civil War.
These panics made Christmas a bad time for many slaves, who passed their Christmases in great fear that they would be rounded up and killed.
What’s changing
Some southern historic plantations and mansions are beginning to include a more accurate history of slavery in their presentations of the past.
Montpelier, the Virginia plantation of U.S. president James Madison and Monticello, the famed mansion and plantation of Thomas Jefferson, for example, have been making efforts for several years now to work more accurate presentations.
Yet another onetime slave-owning president’s preserved site, James Monroe’s Highland, likewise is striving to provide a far more comprehensive look at the enslaved people who once lived there and the conditions they experienced.
There are signs that such changes are taking place elsewhere too. In 2013, for example, the Ben Lomond plantation in Virginia featured in its holiday programming the tale of how enslaved people murdered the place’s owner over Christmas. That same year, Montpelier, once home to President James Madison, asked its interpretors at Christmas to explain to visitors that whites living nearby were afraid of violence by Madison’s slaves.
Christmas programming, however, is changing more slowly than programming at other times of the year. That is because many would like the holiday event to be a fun one.
But a public acknowledgment that slavery was immoral, horrific and resisted by its victims in the form of more sensitive and informative Christmas events at historic mansions and plantations might just be a step toward racial reconciliation in the U.S.
Robert E. May, Professor Emeritus of History, Purdue University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
